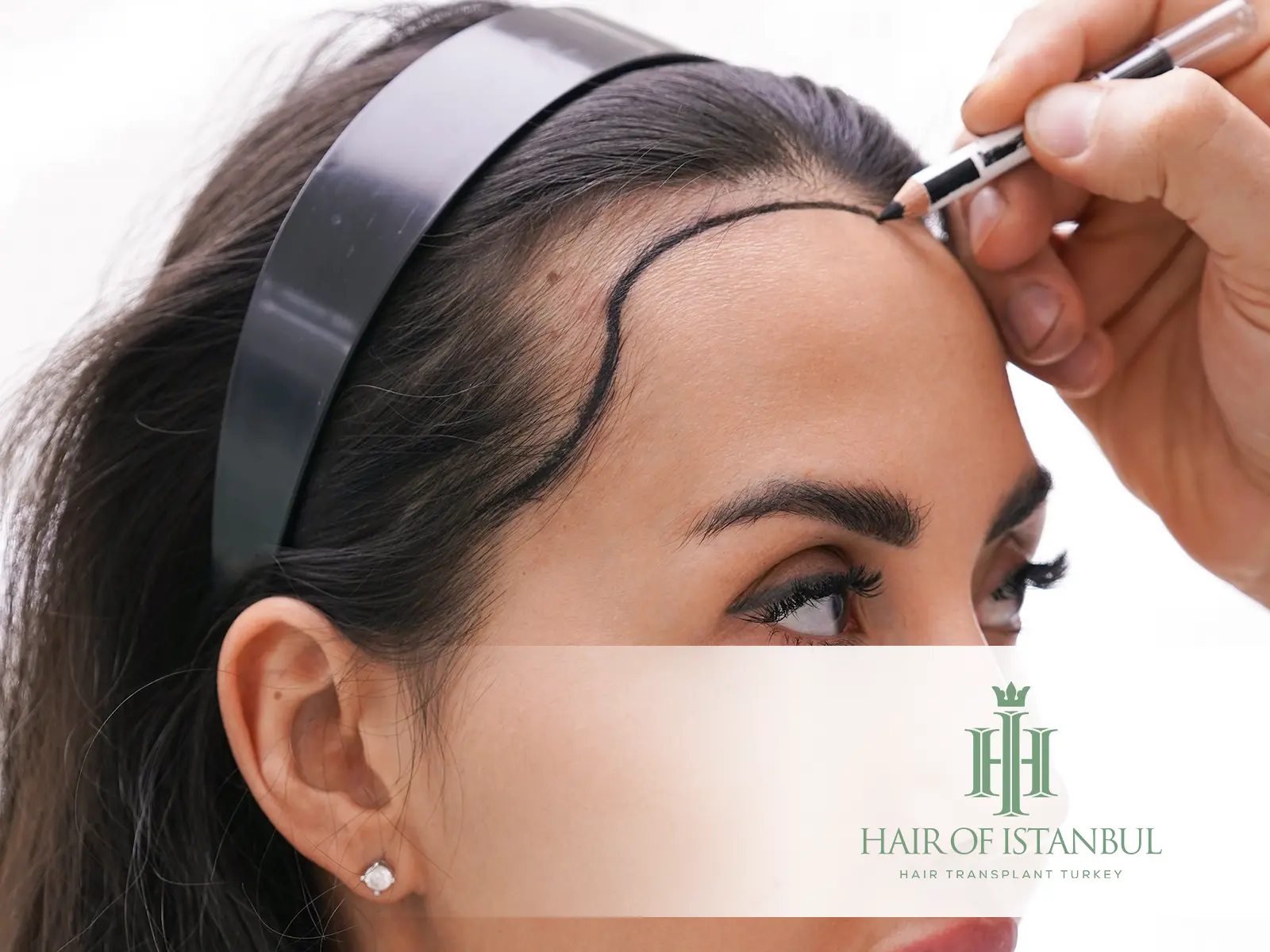

Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Explained: Signs, Causes, and Modern Treatment Approaches
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is a form of scarring alopecia that causes gradual and permanent hair loss along the frontal hairline and temples. It most commonly affects postmenopausal women but can also be seen in men and younger individuals.
As the condition progresses, it can cause both physical and emotional distress. The loss of eyebrow hair is often the first visible sign. Early detection and medical intervention are key to halting its progression and minimizing long-term hair loss.
What Is Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia?
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is a chronic inflammatory condition that leads to the destruction of hair follicles in the frontal scalp region. As follicles are damaged, they are replaced with scar tissue, making the hair loss irreversible in affected areas.
While it was once considered rare, its incidence has risen significantly over the past two decades. The condition typically presents as a symmetric recession of the hairline, giving a distinctive pattern that helps in clinical identification.

Recognizable Symptoms
The most visible sign of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is a receding hairline that starts at the forehead and gradually progresses backward. This can be accompanied by redness, scaling, and itching along the hairline.
Eyebrow thinning or complete loss often precedes the scalp symptoms. In some cases, patients also report a shiny or smooth appearance of the affected skin, along with visible veins near the temples.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is not yet fully understood. However, autoimmune responses, hormonal changes particularly decreased estrogen and genetic factors are believed to contribute significantly.
Environmental factors, including the use of certain skincare products and sunscreens, have also been studied as possible triggers. Research is ongoing, and the condition’s root causes may vary between individuals.
Diagnosis Process
Diagnosis involves a detailed physical examination and dermatoscopic evaluation by a hair restoration specialist. A biopsy may be recommended in some cases to confirm follicular scarring and inflammation.
Early diagnosis of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia increases the chances of preserving existing hair. Clinics like Hair of Istanbul offer expert evaluation and tailor treatment based on the individual’s condition and hair loss history.
Treatment Options and Medical Management
There is currently no cure for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, but several treatments can help stop or slow its progression.
These include:
-
Topical corticosteroids
-
Oral anti-inflammatory medications
-
Hormonal treatments such as anti-androgens
-
Immunosuppressive therapies in advanced cases
Consistency and long term follow-up are essential to monitor the disease’s activity and prevent further follicular damage. At Hair transplant clinic, patients receive long term care protocols designed for inflammatory alopecias.

Is Hair Transplantation a Solution?
In stabilized cases where the condition has been inactive for a significant period, hair transplantation may be considered. This should be evaluated with caution, as scarring skin may not always support graft survival.
If the patient is a candidate, hair transplant surgery can help reconstruct the natural hairline. Female patients with FFA may benefit from hair transplant for women approaches, customized to accommodate frontal thinning patterns.
Before and After Hair Transplant
Visualizing transformation is often helpful. Before and after hair transplant photos illustrate the aesthetic improvements that can be achieved even in difficult cases like Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, if managed correctly.
Such results are only possible when surgery is performed after confirming that the disease is no longer active.
Everyday Management and Lifestyle Considerations
Patients with Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia should be cautious with hair and skincare products. Harsh shampoos, excessive heat styling, and direct sun exposure may aggravate scalp sensitivity.
Emotional impact is also significant. Many individuals experience frustration and anxiety due to changes in their appearance. Psychological support or counseling can help patients adjust and maintain confidence during the treatment journey.
Ongoing Care and Follow-up
Even after treatment, ongoing monitoring is critical to detect any reactivation of the condition. Periodic checkups and dermoscopic evaluations should be part of the long term plan.
Proper post operative routines, such as those outlined in hair transplant care after, are equally essential for patients who undergo surgery, ensuring optimal recovery and maintenance of results.
Conclusion
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is a serious condition that demands early intervention, professional guidance, and consistent care. While it may not be reversible, its progression can be managed effectively with the right treatment and lifestyle support.
If you’ve noticed eyebrow thinning or frontal hairline recession, consult the team at Hair of Istanbul for a personalized evaluation and long-term care plan.
 en
en TR
TR  SK
SK  ITA
ITA  FR
FR  DE
DE  ES
ES  BG
BG 