
Donor Area for Hair Transplant: The Complete 2025 Guide to Density, Safety, and Long-Term Planning
The donor area for hair transplant is the true foundation of every successful procedure. While the recipient area often receives the spotlight, up to 80% of the final result quality depends on the health, density, and long-term preservation of the donor region. Whether the goal is natural density, lifetime durability, or minimal scarring, everything begins with evaluating and managing the donor zone with scientific precision. This guide explains how the donor area determines outcomes, how FUE extraction preserves its appearance, and what patients must know to protect it for life.
Why the Donor Area Determines 80% of Hair Transplant Results
Modern research consistently confirms that the donor area for hair transplant plays a decisive role in surgical success. High-density, stable follicles create strong grafts, which in turn improve survival rates and long-term density. Even the most advanced implantation techniques—whether DHI, Sapphire, or Slit—can only perform as well as the grafts harvested. Simply put, an excellent donor zone enables excellent results; an overharvested one limits all future possibilities.
Leading clinics worldwide therefore prioritise conservative extraction, multi-zone harvesting, and long-term planning strategies that preserve donor integrity for decades rather than just a single session.
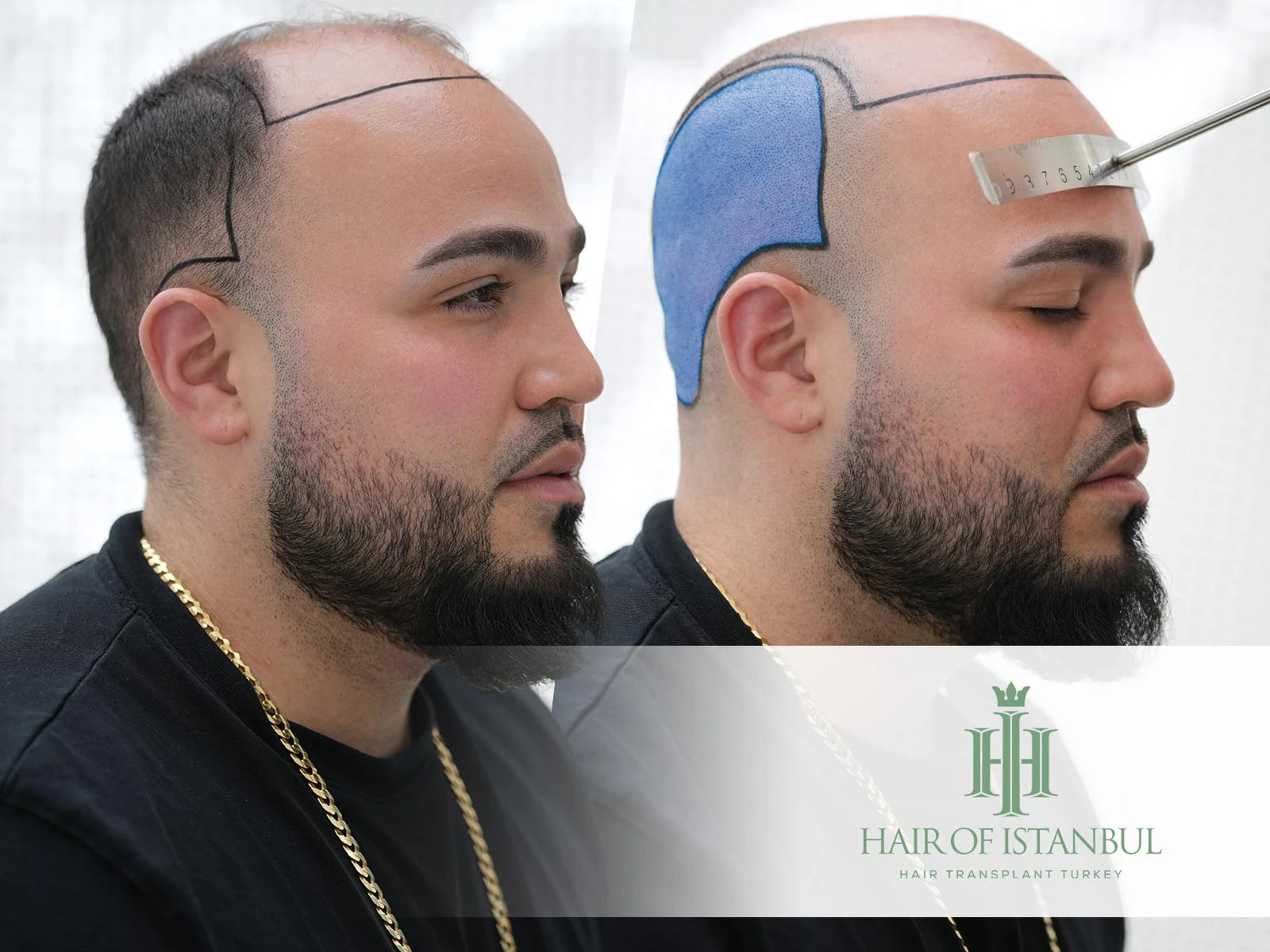
What Defines the Donor Area for Hair Transplant?
The donor region typically includes the occipital and parietal zones—the back and sides of the scalp—where follicles are genetically resistant to DHT, the hormone responsible for male pattern hair loss. These follicles retain their resistance even after transplantation, ensuring permanent growth in the recipient zones.
Key Characteristics of the Donor Area
- DHT-resistant follicles that maintain long-term durability
- A genetically stable “safe zone” approximately 25–30 cm in vertical height
- Consistent follicular grouping (mostly 2–3 hair grafts)
- Strategic density distribution suitable for extraction
Before surgery, clinics perform density mapping, follicular group analysis, miniaturization evaluation, and scalp elasticity testing to determine exactly how many grafts can be extracted safely. These assessments define whether a patient is suitable for the FUE technique and how many future sessions can be planned.
Scientific Findings on Donor Area Density
Dermatological studies show that average donor density typically ranges from 65–85 FU/cm². Individuals below 60 FU/cm² may still qualify for surgery, but long-term coverage may require multi-session strategies or supplemental donor sources such as beard or chest hair.
According to global surgical literature, exceeding safe extraction limits leads to thinning, patchiness, and reduced donor elasticity. This is why the donor area for hair transplant must always be approached with conservative planning and ethical extraction strategies.
Why FUE Is the Gold Standard for Donor Preservation
The FUE method revolutionised donor management by replacing the linear scars of FUT with micro-punch extractions as small as 0.7 mm. During FUE, each follicular unit is extracted individually and distributed evenly across the donor zone. This protects visual density and prevents “patchy” appearance.
Benefits of FUE Extraction
- Minimal scarring thanks to micro-scale punches
- Faster healing—most crusts fall within 7–10 days
- Ability to wear shorter hairstyles
- Even extraction pattern prevents visible thinning
Studies comparing FUT and FUE confirm that FUE significantly reduces long-term scarring and improves patient comfort. The donor area remains visually intact, supporting both aesthetics and future surgical options.
FUT vs. FUE: Why Modern Clinics Prefer FUE
Older FUT techniques required removing a long strip of scalp, which led to a permanent linear scar, reduced scalp flexibility, and longer recovery times. While FUT can still be useful for selected patients, modern clinics prioritize FUE because it:
- Protects natural appearance
- Allows strategic, uniform extraction
- Minimizes discomfort and downtime
- Preserves maximum graft availability
For patients prioritizing aesthetics and discreet healing, the donor area for hair transplant is best maintained with FUE extraction methods.
Understanding Overharvesting and How to Avoid It
Overharvesting occurs when too many grafts are extracted from a concentrated region. This creates empty gaps, reduced visual density, and long-term structural weakening of the donor zone.
Consequences of Overharvesting
- Visible thinning or “see-through” areas
- Irregular density with patchy appearance
- Reduced scalp flexibility
- Compromised blood supply
Responsible surgeons typically extract no more than 20–25% of the total donor capacity per session. When needed, they harvest from multiple zones—including extended donor regions or beard hair—to maintain balance and symmetry.
Healing Timeline of the Donor Area After FUE
Healing begins almost immediately after surgery. Small scabs form at each extraction site and fall naturally within 7–10 days. Mild redness may last up to 2–3 weeks, depending on skin type.
Typical Healing Stages
- Day 1–3: Mild redness, formation of micro-scabs
- Day 4–10: Scabs gradually fall off
- Week 2–4: Pinkness fades, sensitivity decreases
- Month 1–3: Donor texture returns to near-normal
For full recovery, patients must follow structured aftercare protocols such as those explained in the clinic’s after-care guidelines.
Scientific Evidence on Minimal Scarring
Peer-reviewed studies confirm that FUE with punch sizes under 0.9 mm produces negligible scarring visible to the naked eye. Tissue regeneration and collagen remodeling typically restore the donor area’s natural texture within one month.
Why Donor Area Preservation Is Critical for the Future
Hair loss is progressive. A patient who undergoes a successful first surgery may still experience thinning in native areas years later. If the donor area for hair transplant is not preserved, future touch-up sessions may not be possible.
Strategic donor preservation ensures lifelong flexibility: reinforcement sessions, density upgrades, or new design requirements (such as temporal peaks or crown refinements) can be performed without risking donor depletion.
How Surgeons Evaluate Donor Area Health
High-quality clinics use digital imaging, trichoscopy, and AI-assisted measurement to evaluate:
- Follicular density per cm²
- Miniaturization ratio
- Hair shaft calibre
- Growth angle consistency
- Scalp elasticity
This information determines whether the patient is a strong FUE candidate or requires preparatory medical therapy before extraction.
Protecting the Donor Area After Surgery
Postoperative care defines how well the donor area for hair transplant recovers. Key rules include:
- Wash gently with medical shampoo
- Avoid scratching or friction
- Use saline spray for hydration
- Sleep with head elevated for 3–5 nights
- Avoid tight hats and helmets
- Avoid gym, sauna, pool for at least three weeks
Within 10–14 days, most patients resume daily routines with minimal signs of surgery.
Role of Technology in Donor Zone Precision
Modern technologies—micromotor punches, digital density mapping, vacuum-assisted extraction, and robotic imaging—improve precision and uniformity in donor harvesting. Combined with surgical expertise, these tools ensure maximum graft yield with minimal trauma.
Patient Education: Understanding Your Donor Capacity
Informed patients make better decisions. Understanding the limits of your donor area prevents unrealistic expectations and ensures ethical planning. Patients should always ask:
- How many grafts can be safely extracted?
- What percentage of donor density will remain?
- How many sessions can be planned over a lifetime?
Clinics with transparent practices typically explain extraction patterns and show digital simulations before surgery.
External Scientific Reference
For independent medical information on hair loss and scalp conditions, consult the NHS hair loss resource.
Conclusion
The donor area for hair transplant is not only the starting point—it is the key determinant of naturalness, density, longevity, and future flexibility. Conservative FUE extraction, strategic planning, structured aftercare, and long-term preservation ensure that the donor zone remains healthy for life. The science is clear: protect your donor area, and your results will reward you for decades.
It refers to the back and sides of the scalp where follicles are genetically resistant to DHT and suitable for permanent transplantation.
Usually 20–25% of total density per session. This varies by individual density and long-term planning.
No—when performed correctly with micro-punches, FUE preserves natural appearance and leaves minimal scarring.
Initial healing occurs in 7–10 days; full texture recovery generally takes 1–3 months.
In some cases, yes—through micro-FUE redistribution or beard graft supplementation. But prevention is the best strategy.
 en
en TR
TR  SK
SK  ITA
ITA  FR
FR  DE
DE  ES
ES  BG
BG