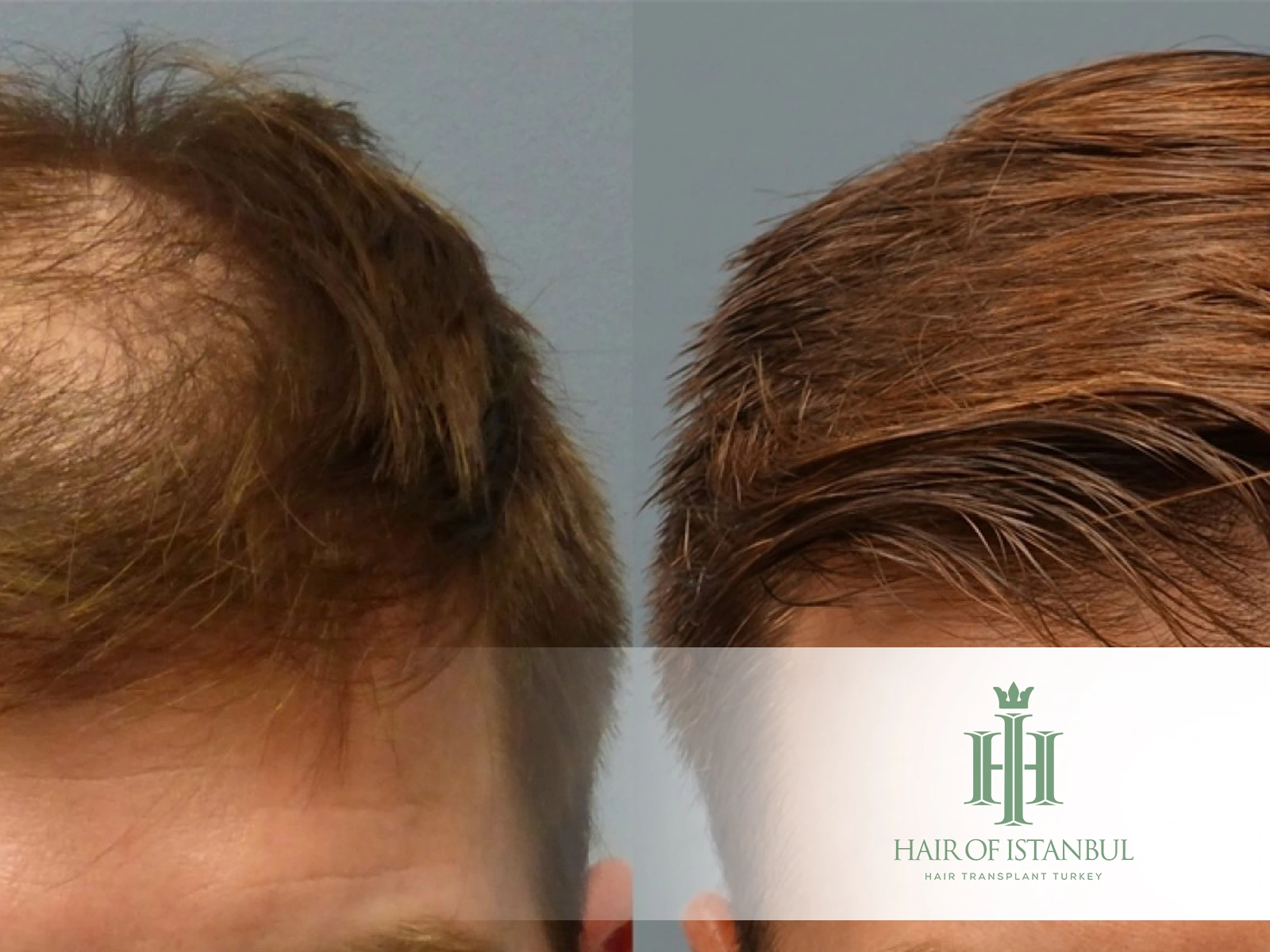
FUT Hair Transplant: Complete 2025 Guide to the Strip Method and Why Modern Clinics Prefer FUE
FUT hair transplant—also known as the “strip method”—is one of the earliest surgical techniques developed for hair restoration. Before the evolution of modern FUE-based extraction, FUT was considered the industry standard for many years. Today, while some clinics still perform FUT, most international centers have transitioned to FUE due to its superior healing profile, minimal scarring, improved comfort, and long-term donor protection.
At Hair of Istanbul, we do not perform the FUT technique. Our medical team exclusively uses FUE extraction combined with implantation methods such as DHI, Sapphire, or Slit. This approach ensures natural results, rapid healing, and long-term donor sustainability—all of which align with the current global standards of modern hair restoration.
What Is a FUT Hair Transplant?
In a FUT hair transplant (Follicular Unit Transplantation), a long strip of skin is surgically removed from the back of the scalp. This strip—typically 15–25 cm long and 1–1.5 cm wide—is dissected under a microscope to create follicular units, which are then implanted into the thinning or bald areas.
The FUT Procedure Step-by-Step
- A linear strip of scalp tissue is surgically removed from the donor area
- The wound is closed with stitches or staples
- The strip is dissected into grafts under magnification
- Recipient sites are created in the transplant area
- Grafts are placed into the recipient incisions
While effective in its time, FUT is significantly more invasive than modern FUE extraction.
Why FUT Leaves a Permanent Linear Scar
The most defining characteristic of FUT is the linear scar left in the donor area. Even if hair grows long, the scar can become visible during short hairstyles or under certain lighting conditions. Some patients also experience tightness, reduced scalp elasticity, or long-term sensitivity in the donor region.
This is a primary reason FUE has overtaken FUT worldwide: FUE leaves tiny dot-like scars instead of a long visible line.
Advantages of FUT Hair Transplant
Although less commonly used today, FUT offers several advantages in specific cases:
- High graft yield in a single session due to strip harvest
- Microscopic dissection allows clean graft preparation
- Useful for select patients with extremely dense donor regions
These benefits, however, are overshadowed by the clear advantages of FUE for the majority of modern patients.
Disadvantages of FUT Hair Transplant
The decline of FUT in modern practice is driven by several drawbacks:
- Permanent linear scar in the donor area
- Longer recovery due to sutures and surgical incision
- Higher post-operative discomfort and tightness
- Limited hairstyle choices (buzzcuts expose the scar)
- Reduced scalp elasticity after strip excision
- Greater overall invasiveness
These factors make FUT far less appealing compared to minimally invasive FUE.
FUT vs FUE: Why Modern Clinics Prefer FUE
Across Europe, the UK, the US, and Turkey, FUE has become the dominant extraction method due to its safety, comfort, and natural healing pattern. FUE provides advantages such as:
- No linear scar—only tiny dot scars
- No stitches or staples
- Faster recovery (most patients resume normal life in 5–7 days)
- Ability to harvest grafts evenly and strategically
- Better donor preservation and aesthetics
- Ideal for short hairstyles
Furthermore, FUE extractions seamlessly support advanced implantation methods such as DHI, Sapphire, or Slit, enabling precise hairline creation and high-density designs.
For these reasons, Hair of Istanbul does not offer FUT hair transplant and exclusively performs FUE-based procedures.
Is FUT Hair Transplant Still Used Today?
Despite its downsides, FUT is still used in limited cases, including:
- Patients with extremely high donor density seeking maximum graft numbers
- Academic or research-based transplantation protocols
- Cases where FUE alone cannot meet graft requirements
However, these situations are rare. The overwhelming majority of clinics worldwide now perform FUE as the primary extraction method.
Healing Timeline for FUT Hair Transplant
Because FUT involves surgical excision and suturing, its healing timeline is longer than FUE:
Typical Healing Stages
- Days 1–3: Tightness, discomfort, and swelling around the incision line
- Days 7–14: Removal of stitches or staples
- 1 Month: Reduction in tension and sensitivity
- 3–6 Months: Linear scar fades gradually but remains permanent
By contrast, FUE patients typically return to social life within a week. For more information on the recovery process, see our guide to modern hair transplant techniques.
Scarring Differences: FUT vs FUE
FUT guarantees a linear scar, while FUE leaves micro-sized dot scars distributed evenly across the donor region. This is why FUE is significantly better suited for people who prefer short hairstyles or want maximum donor aesthetics.
For a deeper explanation of donor zone management, visit the guide on donor area for hair transplant.
Does FUT Hurt More Than FUE?
Yes. Since FUT requires removal of a skin strip and suturing, post-operative tension and pain levels are generally higher. FUE avoids this by using small circular punches instead of an incision. For a broader discussion on discomfort levels during transplantation, explore our guide does hair transplant hurt?.
Sports and Activity After FUT
Because the incision must remain protected, contact sports, weightlifting, and high-intensity workouts are restricted for a longer period after FUT. FUE patients typically resume activity much sooner. Details can be found in the article on exercise after hair transplant.
Long-Term Considerations
FUT can reduce donor flexibility and limit options for future procedures. A long linear scar may intersect with later donor harvesting zones, affecting long-term planning. FUE, on the other hand, offers far greater flexibility for secondary sessions thanks to its distributed extraction pattern.
Independent Medical Reference
For general medical information about hair loss, you can refer to the authoritative NHS hair loss resource.
Conclusion
FUT hair transplant was an important milestone in hair restoration history, but modern practice has shifted decisively toward minimally invasive FUE. With no linear scar, faster healing, and improved comfort, FUE-based extraction—combined with DHI, Sapphire, or Slit implantation—provides superior aesthetics and long-term donor protection. In alignment with global standards, Hair of Istanbul performs only FUE extractions and does not offer the FUT technique.
A strip of scalp is surgically removed and dissected into grafts, leaving a permanent linear scar.
Because FUE provides faster healing, minimal scarring, and better long-term donor preservation.
Yes, but only in limited cases requiring extremely high graft counts.
Yes. FUT involves an incision and sutures, resulting in more post-operative discomfort.
FUE-based extraction with DHI, Sapphire, or Slit implantation is the global gold standard.
 en
en TR
TR  SK
SK  ITA
ITA  FR
FR  DE
DE  ES
ES  BG
BG