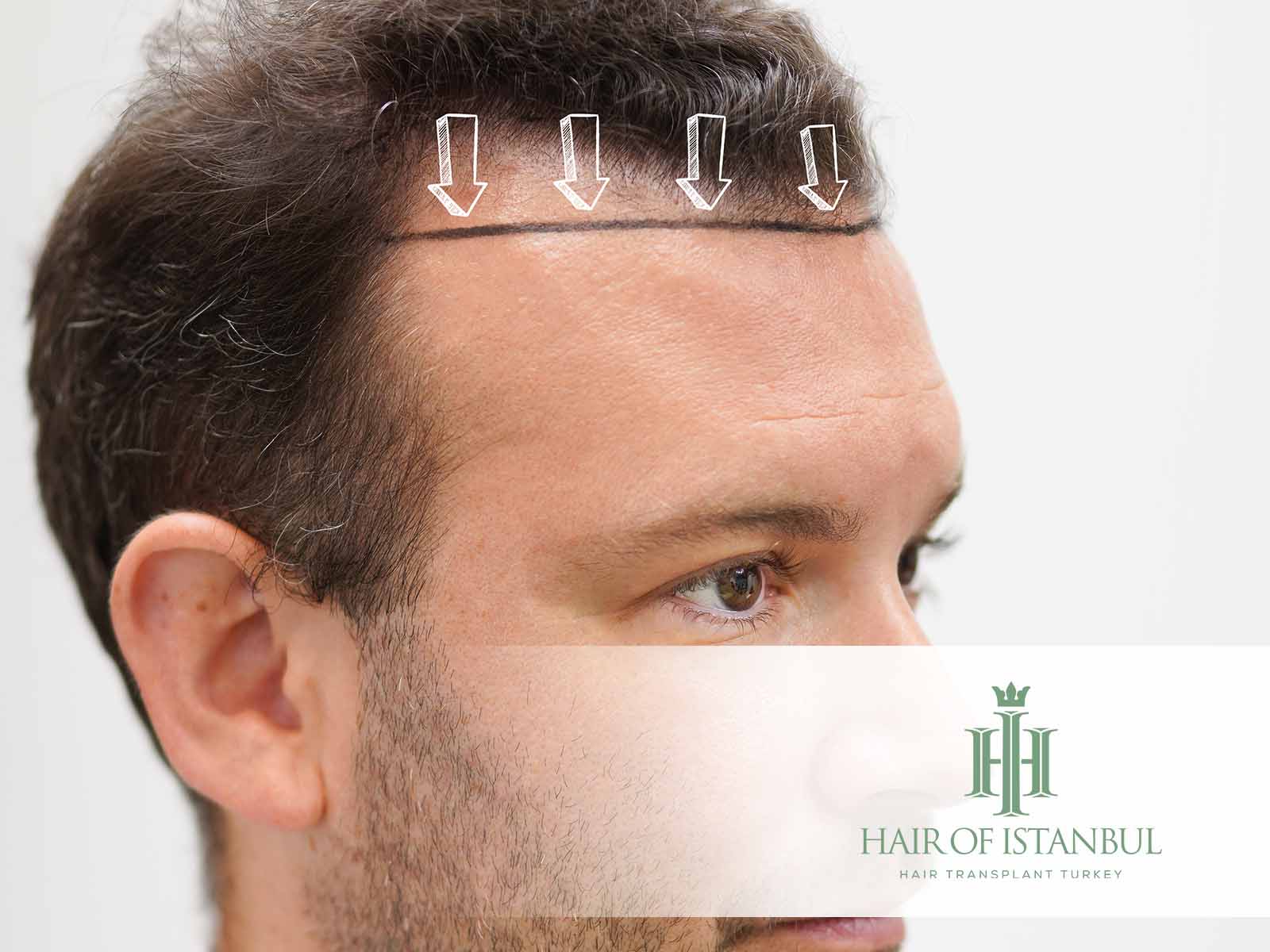
Receding Hairline: Complete 2025 Guide to Causes, Diagnosis, and Hair Transplant Solutions
A receding hairline is one of the earliest and most visible signs of pattern hair loss, affecting millions of men and women worldwide. It often begins subtly—slight temple recession, thinning at the frontal corners, or an uneven hairline contour—but becomes more noticeable over time. Fortunately, modern FUE-based hair transplantation combined with advanced implantation methods such as DHI, Sapphire, or Slit provides natural, permanent, and scientifically guided solutions for restoring the frontal hairline.
This comprehensive 2025 guide explains the causes of a receding hairline, how to identify progression patterns, which treatments work, and how modern hair transplant techniques create natural, long-lasting results.
What Is a Receding Hairline?
A receding hairline occurs when the frontal hairline gradually moves backward, typically starting at the temples. While it is most common in men, women may also experience it due to genetics, hormonal changes, or traction-related damage.
A receding hairline can lead to:
- Visible temple recession
- Uneven or asymmetric hairline shape
- Widening of the forehead
- Thinning of the frontal zone
Understanding the underlying cause determines the correct treatment path.

Main Causes of a Receding Hairline
The most common cause is androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern hair loss), but several additional factors can contribute:
- Genetics: Family history of recession
- DHT sensitivity: Hormone-driven follicle miniaturisation
- Aging: Natural hair thinning
- Stress: Telogen effluvium-related loss
- Traction alopecia: Hairstyles causing repeated tension
- Hormonal changes: Thyroid imbalance, pregnancy, menopause
Proper diagnosis prevents misinterpretation of temporary shedding cycles and ensures patients select the right long-term solution.
How to Identify a Receding Hairline
Patients often notice recession gradually. Common early signs include:
- Deepening of temple corners
- Triangular gaps in the frontal zone
- M-shaped hairline pattern
- Reduced density along the front
A dermatologist or hair transplant doctor can evaluate miniaturisation patterns, donor capacity, and overall progression.
When Is a Hair Transplant Needed for a Receding Hairline?
Not every receding hairline requires immediate surgical correction. Mild recession may respond to medical treatments, but a transplant becomes ideal when:
- The hairline shape is visibly altered
- Temple recession progresses despite medication
- The frontal zone density is noticeably reduced
- The patient desires a stronger, more youthful hairline
Modern transplants provide permanent correction because donor follicles are genetically resistant to DHT.
Hair Transplant Options for a Receding Hairline
All modern hair transplants rely on FUE extraction, which allows individual follicular units to be harvested with minimal scarring. Implantation may then be performed using different tools and strategies.
1. FUE Extraction
This is the foundation of all modern procedures. Using micro-punches, surgeons extract grafts individually from the donor area. Learn more about this method in our FUE technique guide.
2. DHI Implantation
DHI pens allow direct, angle-controlled implantation, making them ideal for creating a soft, natural, low-angle hairline.
3. Sapphire and Slit Implantation
These methods use micro-channels to guide the correct angulation and density for high-precision results.
Designing a Natural Hairline
Building a natural hairline requires a combination of medical expertise and artistic precision. Key principles include:
- Irregular micro-variation: Natural hairlines are never perfectly straight
- Single-hair grafts: Used exclusively for the front 1–2 rows
- Gradual density increase: Prevents an artificial “wall-like” look
- Correct angulation: 10–15° for natural framing
Hairline artistry is a critical skill. A poorly designed line may appear artificial even with perfect graft growth.

How Many Grafts Are Needed for a Receding Hairline?
The number of grafts depends on the degree of recession:
- Mild recession: 800–1,200 grafts
- Moderate temple loss: 1,200–1,800 grafts
- Advanced recession: 1,800–2,500+ grafts
Accurate graft planning requires donor evaluation, explained in detail in the donor area guide.
Recovery Timeline After a Hairline Transplant
The recovery process follows a predictable biological cycle:
Days 1–10
- Scabbing and early healing
- Redness in the frontal zone
- Grafts stabilise
First washing rules are explained in the first wash after hair transplant guide.
Weeks 2–6
- Shock loss (temporary shedding)
- Follicles rest beneath the skin
Months 3–6
- Early growth begins
- Fine, soft hairs emerge
This stage is discussed in the hair transplant after 3 months article.
Months 6–9
- Visible density improvement
- Directional refinement
- Stronger texture
Months 12–18
- Full maturation
- Peak density and natural blending
A receding hairline transplant should be evaluated only after complete maturation.
Non-Surgical Treatments for a Receding Hairline
While transplants provide permanent correction, some cases benefit from supportive medical therapy:
- Minoxidil (vasodilator)
- Finasteride or dutasteride (hormonal control for men)
- Low-level laser therapy
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
These therapies help stabilise thinning areas, especially around native hair adjacent to the transplant zone.
Common Mistakes When Treating a Receding Hairline
- Designing an unnaturally low hairline
- Ignoring long-term donor preservation
- Over-packing the temples
- Choosing clinics without medical supervision
- Expecting final results before 12–18 months
When to Worry About a Receding Hairline
Medical evaluation is important if recession:
- Progresses rapidly
- Occurs unevenly
- Is accompanied by inflammation or scarring
- Follows major physical or emotional stress
Independent Medical Reference
For general information on hair loss and scalp conditions, refer to the authoritative NHS hair loss resource.
Conclusion
The receding hairline is one of the most common forms of hair loss, but also one of the most effectively treated with modern FUE-based hair transplantation. With proper diagnosis, artistic hairline design, and strategic donor planning, patients can achieve natural, permanent, and age-appropriate results. Combined with medical therapy when necessary, a receding hairline transplant restores facial framing, balance, and confidence for the long term.
Mainly genetics and DHT-related miniaturisation, but stress and traction can also play a role.
Usually 800–2,500 grafts depending on recession degree.
Yes. Donor follicles are genetically resistant to DHT.
Early growth begins at Months 3–4, full results at 12–18 months.
Mild cases may improve with medications, but moderate-to-severe recession typically requires transplantation.
 en
en TR
TR  SK
SK  ITA
ITA  FR
FR  DE
DE  ES
ES  BG
BG